The Science

L-Arginine and L-Citrulline as Vitamins vs. Nutraceuticals
Are They Vitamins?
- No, arginine and citrulline are not vitamins.
- Vitamins are essential micronutrients required in small amounts that the body either cannot produce or produces insufficiently.
- L-Arginine and L-Citrulline are amino acids, which serve as building blocks for proteins and play roles in physiological functions like nitric oxide (NO) production, circulation, and muscle metabolism.
- L-Arginine: Precursor to nitric oxide, helps with vasodilation, circulation, and immune function.
- L-Citrulline: Converts to arginine in the body, supporting longer-lasting NO production, reducing muscle fatigue, and enhancing athletic performance.
Summary
These products, derived from amino acid and herbal compounds, along with other natural sources, are designed to support overall wellness and enhance bodily functions. Rich in bioactive compounds, nutraceuticals help support healthy immune and digestive functions, enhance mental clarity, and promote heart and joint health. Scientifically formulated, our sublingual provides an effective alternative to traditional supplements
Key Differences
Amino Acids
Building blocks of proteins.
Essential for muscle growth, enzyme production, neurotransmitter function, and overall metabolism.

Vitamins
Organic compounds
required in small amounts
for essential biological processes.

Why Amino Acids Are Not Vitamins
- Vitamins are micronutrients, whereas amino acids are macronutrients.
- Vitamins do not form proteins, while amino acids do.
- The body can synthesize some amino acids but cannot synthesize vitamins in sufficient amounts, requiring dietary intake.
Conclusion
Amino acids and vitamins are both essential for health, but they serve different functions—amino acids build proteins, while vitamins support metabolic and physiological processes.
What is Ginseng?
- Ginseng is an adaptogenic herb, not a vitamin or mineral.
- It contains active compounds called ginsenosides, which have been studied for their potential benefits on energy, cognitive function, and immune support.
- Common types include Asian (Panax) ginseng and American ginseng.
How is it Classified?
- Herbal Supplement: Often used in traditional medicine for its potential stress-reducing and energy-boosting effects.
- Nutraceutical: It provides health benefits beyond basic nutrition, but it is not classified as a vitamin.

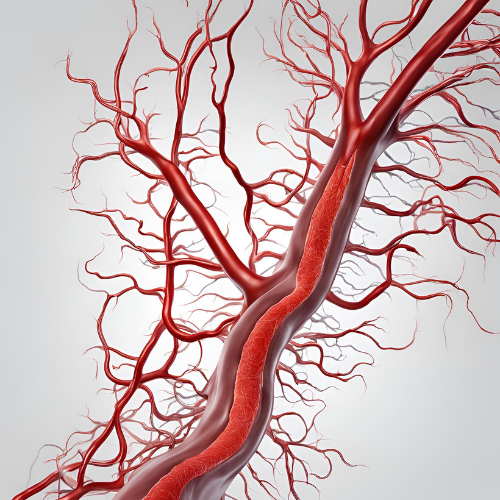
Vasodilation: Definition & Function
Vasodilation is the widening of blood vessels, which increases blood flow and reduces blood pressure. This process occurs when the smooth muscles in the blood vessel walls relax, allowing the vessels to expand.
Causes of Vasodilation

Biological Signals
Nitric Oxide (NO):
A key molecule that relaxes blood vessels shown to support by L-Arginine and L-Citrulline).
Prostaglandins:
Lipid compounds that help regulate inflammation and circulation.
Histamine:
Released in allergic reactions, increasing blood flow to affected areas.

External Triggers
Exercise:
Muscles demand more oxygen, triggering vasodilation.
Heat:
Expands blood vessels to release excess heat.
Dietary Compounds:
Certain foods and supplements (e.g., L-Arginine, L-Citrulline, ginseng, cayenne pepper)
enhance vasodilation.
Benefits of Vasodilation
- Improved Circulation: Helps oxygen and nutrients reach tissues more efficiently.
- Lower Blood Pressure: Reduces strain on the heart and arteries.
- Enhanced Physical Performance: Increases blood flow to muscles during exercise.
- Better Cognitive Function: Improved brain oxygenation can enhance focus and memory.
Vasodilation & Supplements
- L-Arginine & L-Citrulline: Boost nitric oxide production.
- Ginseng: May enhance circulation and cardiovascular health.
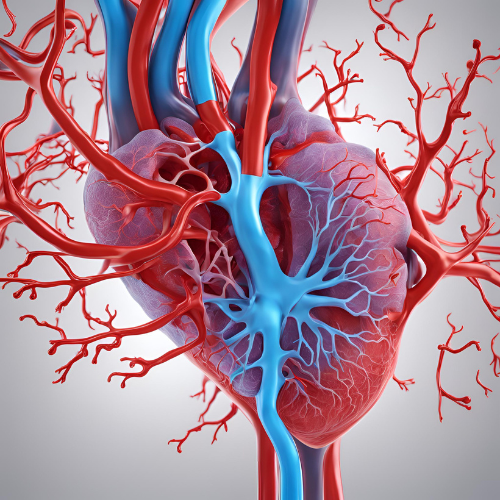
How L-Citrulline Converts to L-Arginine
- L-Citrulline is absorbed in the intestines and taken up by the kidneys.
- Inside the kidneys, L-Citrulline is converted into L-Arginine via enzymatic processes.
- The newly synthesized L-Arginine is then used to produce nitric oxide (NO), which promotes vasodilation, improving blood flow and circulation.
Why L-Citrulline May Be More Effective Than L-Arginine
- Better Absorption: L-Arginine breaks down quickly in the gut and liver, limiting how much reaches circulation. L-Citrulline, on the other hand, bypasses this breakdown and leads to higher sustained L-Arginine levels.
- Longer-Lasting NO Production: Since L-Citrulline is converted gradually into arginine, it supports prolonged nitric oxide release, enhancing endurance and cardiovascular benefits.
Key Benefits of L-Citrulline (via L-Arginine Conversion)
Conclusion
L-Citrulline acts as a precursor to L-Arginine, making it a more effective supplement for boosting nitric oxide levels and improving circulation, endurance, and cardiovascular health.

- Enhanced Vasodilation & Blood Flow
- Improved Exercise Performance & Endurance
- Reduced Muscle Fatigue & Better Recovery
- Supports Heart Health & Blood Pressure Regulation
